Meniscus Tears
Meniscus Tears
Meniscus tears are one of the most common type of knee injuries. Those more at risk tend to be athletes and sportsmen who are involved with contact sports. However, anyone can suffer a meniscus tear, regardless of age. Activities that cause the knee to twist forcefully can result in a torn meniscus.
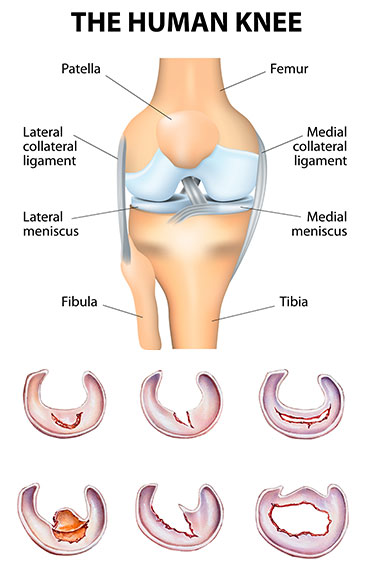
The meniscus is a piece of C -shaped cartilage that provides a cushion between your thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). It also serves as a secondary stabilizer to the knee joint. There are two menisci in each knee and they can be damaged or torn during activities that put pressure on or rotate the knee joint.
Causes of a Meniscus Tear
The meniscus injuries happen mostly during sports activities. Players get injured when there is direct contact or pressure including a forced twist or rotation during sports.
The meniscus also weakens with age and tears (degenerate tears) are more common in people over the age of 50. A simple awkward movement like squatting or getting up from a chair can lead to injury in someone with weak menisci. People with osteoarthritis are at increased risk of injuring their knee or tearing their meniscus due to tissue degeneration with minimal or no trauma.
Symptoms of a Meniscus Tear
When a meniscus tear occurs, you might feel a “pop” in your knee. Most patients can still walk on the injured knee, but the knee often becomes more painful, stiff and swollen gradually. The more common symptoms of a meniscus tear are:
- Localised pain around the knee
- Swelling around the knee.
- Difficulty moving the knee or inability to move it in a full range of motion
- Catching or locking of the knee.
- Sensation of “instability” or “giving way”
Without treatment, the meniscus tear can propagate and worsen. A piece of meniscus can also become loose and drift in between the bones of the joint causing the knee to pop or lock.
Meniscus Tear: Diagnosis
Physical Exam
After taking a medical history and understanding your symptoms, your doctor will examine your knee and test your range of motion, paying attention to the spot where the meniscus is along your joint. Imaging tests may be ordered to confirm a tear of the meniscus, including
Knee X-Ray
This test will not show a meniscus tear. However, it can be helpful to determine if there are any other causes of your knee pain, like osteoarthritis.
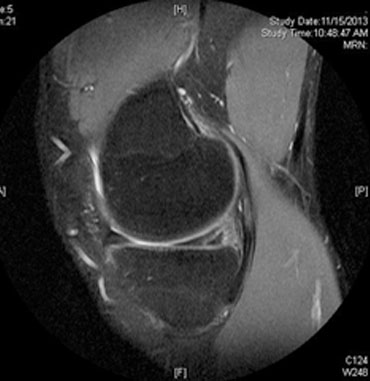
MRI
An MRI uses a magnetic field to take multiple images of your knee. This is a type of detailed scan and it will be able to show images of the soft tissue in the knee and determine if there’s a meniscus tear.
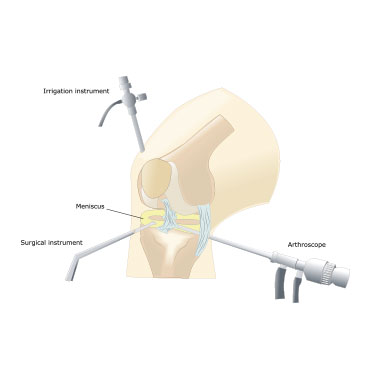
Arthroscopy
In some situations, the doctor might recommend using an instrument called an arthroscope to examine the inside of your knee. This involves making a small incision near the knee. The arthroscopic is inserted through this incision. The decide is a small camera and it allows transmission of the image of the inside of your knee onto a monitor. Whenever necessary, special surgical instruments can be inserted through additional incisions to the knee to fix the meniscus tear at the same time.
Treatment Options
Treatment of the meniscus tear will depend on the type of tear you have, its location, complexity and size.
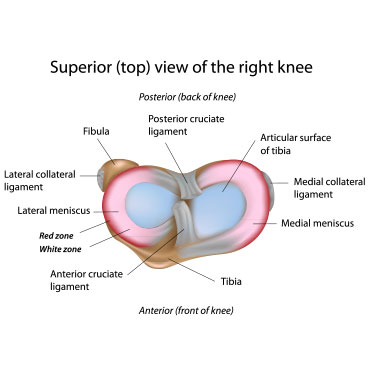
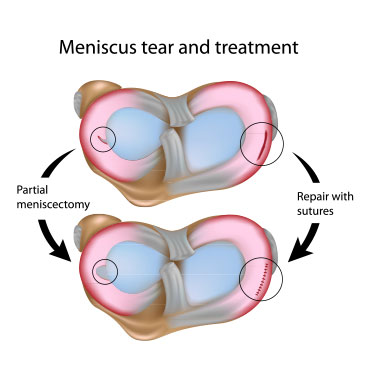
A small, stable tear in the periphery of the meniscus can be treated non- surgically and allowed to heal on its own. A tear in this area known as the “Red Zone” because it has a rich blood supply. In contrast, a tear in the inner two thirds, also known as the “White Zone” has poor blood supply and cannot heal. Tears in these zones can propagate and are usually surgically trimmed away.
Your individual treatment plan will also be customized in accordance to your age, activity level and other related injuries along with the type of meniscus tear you have.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Meniscus Tear
If your tear is small, stable and on the outer edge of the meniscus, it may be possible to be treated non- surgically. Tears associated with arthritis are also treated non- surgically as they tend to improve over time with treatment of the arthritis.
Recommended treatment plans include:
- Rest. Take a break and avoid activities that aggravate the knee pain. Using a walking aid or crutches can help.
- Ice. Ice can help to reduce the pain and swelling in the knee. It is most useful for the initial 2 days. Use a cold pack or a bag of ice, with a towel over and ice the affected knee for about 10- 15 minutes at a time.
- Compression. To prevent additional swelling, using an elastic compression bandage. This can also help ease the discomfort in the knee.
- Elevation. To help reduce swelling, keeping the affected leg elevated on a single pillow when lying down.
- Medications. Anti- inflammatory medications such as Arcoxia can help with the pain and inflammation in the affected knee joint.
Surgical Treatment for Meniscus Tear
Surgical treatment for meniscus tear is recommended when the knee remains painful or symptomatic despite non-surgical treatment. Surgery is also recommended if the knee locks and is unable to achieve the full range of motion.
During surgery, the meniscus will be surgically trimmed with specialized instruments if it is unable to be repaired.
Knee arthroscopy is one of the most commonly performed procedure for treatment of meniscus tears. It is also known as minimally invasive surgery or key hole surgery. A small incision will be made in your knee and the orthopedic surgeon will insert tools and a camera through the incision to repair or trim away the damaged meniscus. The entire procedure typically lasts about an hour. You can usually go home the same day after this procedure or stay 1 night in hospital.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
After surgery, your knee might be placed in a brace to limit the range of motion. Crutches are needed to help reduce the weight on the affected knee. Once the initial healing is complete, rehabilitation exercises are prescribed to restore mobility and strength to your knee.

Why Choose Us?
Dr. Deepak Kumar and Dr. Neetu Gagneja are an experienced orthopaedic surgeon who specializes in
Meniscus Tears
They will assess your condition and advise the best form of treatment for your condition. With proper treatment, patients can look forward to a full and quick recovery without complications.

